diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 6a9bec40..21341913 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -9,7 +9,8 @@ tools that do one thing well.
This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
[ruby-build](https://github.com/sstephenson/ruby-build), and modified for Python.
-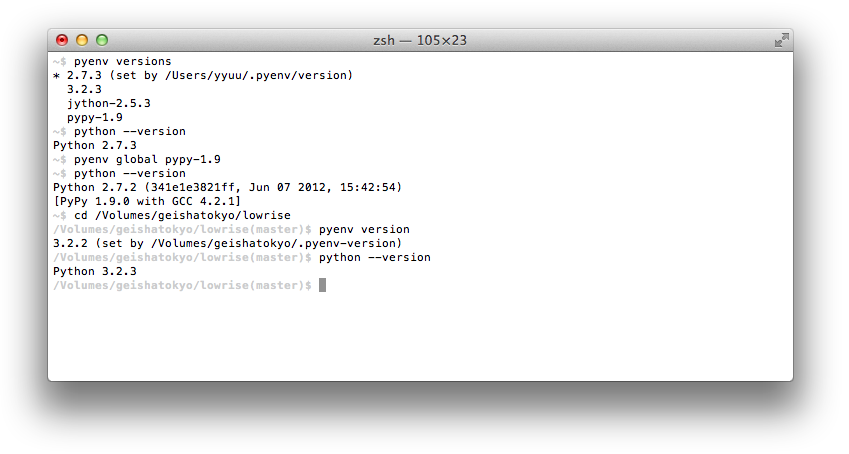 +
+ +
### pyenv _does..._
@@ -20,6 +21,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* Search commands from **multiple versions of Python at a time**.
This may be helpful to test across Python versions with [tox](http://pypi.python.org/pypi/tox).
+
### In contrast with pythonbrew and pythonz, pyenv _does not..._
* **Depend on Python itself.** pyenv was made from pure shell scripts.
@@ -30,6 +32,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
yourself, or [pyenv-virtualenv](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-virtualenv)
to automate the process.
+
## Table of Contents
* [How It Works](#how-it-works)
@@ -56,6 +59,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* [Version History](#version-history)
* [License](#license)
+
## How It Works
At a high level, pyenv intercepts Python commands using shim
@@ -63,6 +67,7 @@ executables injected into your `PATH`, determines which Python version
has been specified by your application, and passes your commands along
to the correct Python installation.
+
### Understanding PATH
When you run a command like `python` or `pip`, your operating system
@@ -78,6 +83,7 @@ precedence over another one at the end. In this example, the
`/usr/local/bin` directory will be searched first, then `/usr/bin`,
then `/bin`.
+
### Understanding Shims
pyenv works by inserting a directory of _shims_ at the front of your
@@ -98,28 +104,30 @@ operating system will do the following:
* Run the shim named `pip`, which in turn passes the command along to
pyenv
+
### Choosing the Python Version
When you execute a shim, pyenv determines which Python version to use by
reading it from the following sources, in this order:
-1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable, if specified. You can use
+1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable (if specified). You can use
the [`pyenv shell`](#pyenv-shell) command to set this environment
variable in your current shell session.
2. The application-specific `.python-version` file in the current
- directory, if present. You can modify the current directory's
+ directory (if present). You can modify the current directory's
`.python-version` file with the [`pyenv local`](#pyenv-local)
command.
-3. The first `.python-version` file found by searching each parent
- directory until reaching the root of your filesystem, if any.
+3. The first `.python-version` file found (if any) by searching each parent
+ directory, until reaching the root of your filesystem.
4. The global `~/.pyenv/version` file. You can modify this file using
the [`pyenv global`](#pyenv-global) command. If the global version
file is not present, pyenv assumes you want to use the "system"
- Python—i.e. whatever version would be run if pyenv weren't in your
- path.
+ Python. (In other words, whatever version would run if pyenv weren't in your
+ `PATH`.)
+
### Locating the Python Installation
@@ -128,39 +136,43 @@ specified, it passes the command along to the corresponding Python
installation.
Each Python version is installed into its own directory under
-`~/.pyenv/versions`. For example, you might have these versions
-installed:
+`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
+For example, you might have these versions installed:
* `~/.pyenv/versions/2.7.6/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/pypy-2.2.1/`
-Version names to pyenv are simply the names of the directories in
+As far as pyenv is concerned, version names are simply the directories in
`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
## Installation
If you're on Mac OS X, consider
[installing with Homebrew](#homebrew-on-mac-os-x).
+
### The automatic installer
Visit my other project:
https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-installer
+
### Basic GitHub Checkout
This will get you going with the latest version of pyenv and make it
easy to fork and contribute any changes back upstream.
-1. Check out pyenv where you want it installed. A good place to choose is
+1. **Check out pyenv where you want it installed.** A good place to choose is
`$HOME/.pyenv` but you may install it somewhere else.
$ cd
$ git clone git://github.com/yyuu/pyenv.git .pyenv
-2. Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT` to point to the path where
+2. **Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT`** to point to the path where
pyenv repo is cloned and add `$PYENV_ROOT/bin` to your `$PATH` for access
to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
@@ -170,19 +182,19 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-3. Add pyenv init to your shell to enable shims and autocompletion.
+3. **Add `pyenv init` to your shell** to enable shims and autocompletion.
$ echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bash_profile
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-4. Restart your shell so the path changes take effect. You can now
+4. **Restart your shell so the path changes take effect.** You can now
begin using pyenv.
$ exec $SHELL
-5. Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`. For example, to
+5. **Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`.** For example, to
install Python 2.7.6, download and unpack the source, then run:
$ pyenv install 2.7.6
@@ -192,12 +204,13 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**NOTE** If you are having trouble installing a python version please visit the wiki page about [Common Build Problems](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/wiki/Common-build-problems)
-6. Rebuild the shim binaries. You should do this any time you install
- a new Python binary (for example, when installing a new Python version,
- or when installing a package that provides a binary).
+6. **Rebuild the shim binaries.** You should do this any time you install
+ a new Python binary. (Examples: installing a new Python version,
+ or installing a package that provides a binary.)
$ pyenv rehash
+
#### Upgrading
If you've installed pyenv using the instructions above, you can
@@ -217,23 +230,24 @@ tag:
v0.1.0
$ git checkout v0.1.0
+
### Homebrew on Mac OS X
You can also install pyenv using the
-[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS
-X.
+[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS X.
~~~
$ brew update
$ brew install pyenv
~~~
-To later update these installs, use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
+To upgrade pyenv in the future, just use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
-Afterwards you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
-profile as stated in the caveats. You'll only ever have to do this
+After installation, you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
+profile (as stated in the caveats). You'll only ever have to do this
once.
+
### Neckbeard Configuration
Skip this section unless you must know what every line in your shell
@@ -243,47 +257,48 @@ profile is doing.
extra commands into your shell. Coming from rvm, some of you might be
opposed to this idea. Here's what `pyenv init` actually does:
-1. Sets up your shims path. This is the only requirement for pyenv to
+1. **Sets up your shims path.** This is the only requirement for pyenv to
function properly. You can do this by hand by prepending
`~/.pyenv/shims` to your `$PATH`.
-2. Installs autocompletion. This is entirely optional but pretty
+2. **Installs autocompletion.** This is entirely optional but pretty
useful. Sourcing `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.bash` will set that
up. There is also a `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.zsh` for Zsh
users.
-3. Rehashes shims. From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
+3. **Rehashes shims.** From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
shim files. Doing this on init makes sure everything is up to
date. You can always run `pyenv rehash` manually.
-4. Installs the sh dispatcher. This bit is also optional, but allows
+4. **Installs the sh dispatcher.** This bit is also optional, but allows
pyenv and plugins to change variables in your current shell, making
commands like `pyenv shell` possible. The sh dispatcher doesn't do
anything crazy like override `cd` or hack your shell prompt, but if
for some reason you need `pyenv` to be a real script rather than a
shell function, you can safely skip it.
-Run `pyenv init -` for yourself to see exactly what happens under the
-hood.
+To see exactly what happens under the hood for yourself, run `pyenv init -`.
+
### Uninstalling Python Versions
-As time goes on, Python versions you install will accumulate in your
+As time goes on, you will accumulate Python versions in your
`~/.pyenv/versions` directory.
To remove old Python versions, `pyenv uninstall` command to automate
the removal process.
-Or, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the
-version you want to remove. You can find the directory of a particular
-Python version with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix
-2.6.8`.
+Alternatively, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the version you want
+to remove. You can find the directory of a particular Python version
+with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix 2.6.8`.
+
## Command Reference
Like `git`, the `pyenv` command delegates to subcommands based on its
first argument. The most common subcommands are:
+
### pyenv local
Sets a local application-specific Python version by writing the version
@@ -304,6 +319,7 @@ file named `.pyenv-version`. For backwards compatibility, pyenv will
read a local version specified in an `.pyenv-version` file, but a
`.python-version` file in the same directory will take precedence.
+
#### pyenv local (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as local Python at once.
@@ -337,6 +353,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv global
Sets the global version of Python to be used in all shells by writing
@@ -352,6 +369,7 @@ The special version name `system` tells pyenv to use the system Python
When run without a version number, `pyenv global` reports the
currently configured global version.
+
#### pyenv global (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as global Python at once.
@@ -385,6 +403,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv shell
Sets a shell-specific Python version by setting the `PYENV_VERSION`
@@ -405,6 +424,7 @@ prefer not to use shell integration, you may simply set the
$ export PYENV_VERSION=pypy-2.2.1
+
#### pyenv shell (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions via `PYENV_VERSION` at once.
@@ -438,6 +458,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv versions
Lists all Python versions known to pyenv, and shows an asterisk next to
@@ -451,6 +472,7 @@ the currently active version.
jython-2.5.3
pypy-2.2.1
+
### pyenv version
Displays the currently active Python version, along with information on
@@ -459,6 +481,7 @@ how it was set.
$ pyenv version
2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
+
### pyenv rehash
Installs shims for all Python binaries known to pyenv (i.e.,
@@ -467,6 +490,7 @@ version of Python, or install a package that provides binaries.
$ pyenv rehash
+
### pyenv which
Displays the full path to the executable that pyenv will invoke when
@@ -475,6 +499,7 @@ you run the given command.
$ pyenv which python3.3
/home/yyuu/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/bin/python3.3
+
### pyenv whence
Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
@@ -483,7 +508,8 @@ Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
2.6.8
2.7.6
3.3.3
-
+
+
### pyenv install
Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-build), this installs versions of python
@@ -494,7 +520,8 @@ Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-
system
2.6.8
* 2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
-
+
+
### pyenv install --list
List available remote versions of Python, including Anaconda, Jython, pypy, and stackless
@@ -511,9 +538,10 @@ and easy to understand, even if you're not a shell hacker.
Please feel free to submit pull requests and file bugs on the [issue
tracker](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/issues).
+
### Version History
-See CHANGELOG.md.
+See [CHANGELOG.md](CHANGELOG.md).
### License
+
### pyenv _does..._
@@ -20,6 +21,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* Search commands from **multiple versions of Python at a time**.
This may be helpful to test across Python versions with [tox](http://pypi.python.org/pypi/tox).
+
### In contrast with pythonbrew and pythonz, pyenv _does not..._
* **Depend on Python itself.** pyenv was made from pure shell scripts.
@@ -30,6 +32,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
yourself, or [pyenv-virtualenv](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-virtualenv)
to automate the process.
+
## Table of Contents
* [How It Works](#how-it-works)
@@ -56,6 +59,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* [Version History](#version-history)
* [License](#license)
+
## How It Works
At a high level, pyenv intercepts Python commands using shim
@@ -63,6 +67,7 @@ executables injected into your `PATH`, determines which Python version
has been specified by your application, and passes your commands along
to the correct Python installation.
+
### Understanding PATH
When you run a command like `python` or `pip`, your operating system
@@ -78,6 +83,7 @@ precedence over another one at the end. In this example, the
`/usr/local/bin` directory will be searched first, then `/usr/bin`,
then `/bin`.
+
### Understanding Shims
pyenv works by inserting a directory of _shims_ at the front of your
@@ -98,28 +104,30 @@ operating system will do the following:
* Run the shim named `pip`, which in turn passes the command along to
pyenv
+
### Choosing the Python Version
When you execute a shim, pyenv determines which Python version to use by
reading it from the following sources, in this order:
-1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable, if specified. You can use
+1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable (if specified). You can use
the [`pyenv shell`](#pyenv-shell) command to set this environment
variable in your current shell session.
2. The application-specific `.python-version` file in the current
- directory, if present. You can modify the current directory's
+ directory (if present). You can modify the current directory's
`.python-version` file with the [`pyenv local`](#pyenv-local)
command.
-3. The first `.python-version` file found by searching each parent
- directory until reaching the root of your filesystem, if any.
+3. The first `.python-version` file found (if any) by searching each parent
+ directory, until reaching the root of your filesystem.
4. The global `~/.pyenv/version` file. You can modify this file using
the [`pyenv global`](#pyenv-global) command. If the global version
file is not present, pyenv assumes you want to use the "system"
- Python—i.e. whatever version would be run if pyenv weren't in your
- path.
+ Python. (In other words, whatever version would run if pyenv weren't in your
+ `PATH`.)
+
### Locating the Python Installation
@@ -128,39 +136,43 @@ specified, it passes the command along to the corresponding Python
installation.
Each Python version is installed into its own directory under
-`~/.pyenv/versions`. For example, you might have these versions
-installed:
+`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
+For example, you might have these versions installed:
* `~/.pyenv/versions/2.7.6/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/pypy-2.2.1/`
-Version names to pyenv are simply the names of the directories in
+As far as pyenv is concerned, version names are simply the directories in
`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
## Installation
If you're on Mac OS X, consider
[installing with Homebrew](#homebrew-on-mac-os-x).
+
### The automatic installer
Visit my other project:
https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-installer
+
### Basic GitHub Checkout
This will get you going with the latest version of pyenv and make it
easy to fork and contribute any changes back upstream.
-1. Check out pyenv where you want it installed. A good place to choose is
+1. **Check out pyenv where you want it installed.** A good place to choose is
`$HOME/.pyenv` but you may install it somewhere else.
$ cd
$ git clone git://github.com/yyuu/pyenv.git .pyenv
-2. Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT` to point to the path where
+2. **Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT`** to point to the path where
pyenv repo is cloned and add `$PYENV_ROOT/bin` to your `$PATH` for access
to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
@@ -170,19 +182,19 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-3. Add pyenv init to your shell to enable shims and autocompletion.
+3. **Add `pyenv init` to your shell** to enable shims and autocompletion.
$ echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bash_profile
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-4. Restart your shell so the path changes take effect. You can now
+4. **Restart your shell so the path changes take effect.** You can now
begin using pyenv.
$ exec $SHELL
-5. Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`. For example, to
+5. **Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`.** For example, to
install Python 2.7.6, download and unpack the source, then run:
$ pyenv install 2.7.6
@@ -192,12 +204,13 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**NOTE** If you are having trouble installing a python version please visit the wiki page about [Common Build Problems](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/wiki/Common-build-problems)
-6. Rebuild the shim binaries. You should do this any time you install
- a new Python binary (for example, when installing a new Python version,
- or when installing a package that provides a binary).
+6. **Rebuild the shim binaries.** You should do this any time you install
+ a new Python binary. (Examples: installing a new Python version,
+ or installing a package that provides a binary.)
$ pyenv rehash
+
#### Upgrading
If you've installed pyenv using the instructions above, you can
@@ -217,23 +230,24 @@ tag:
v0.1.0
$ git checkout v0.1.0
+
### Homebrew on Mac OS X
You can also install pyenv using the
-[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS
-X.
+[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS X.
~~~
$ brew update
$ brew install pyenv
~~~
-To later update these installs, use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
+To upgrade pyenv in the future, just use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
-Afterwards you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
-profile as stated in the caveats. You'll only ever have to do this
+After installation, you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
+profile (as stated in the caveats). You'll only ever have to do this
once.
+
### Neckbeard Configuration
Skip this section unless you must know what every line in your shell
@@ -243,47 +257,48 @@ profile is doing.
extra commands into your shell. Coming from rvm, some of you might be
opposed to this idea. Here's what `pyenv init` actually does:
-1. Sets up your shims path. This is the only requirement for pyenv to
+1. **Sets up your shims path.** This is the only requirement for pyenv to
function properly. You can do this by hand by prepending
`~/.pyenv/shims` to your `$PATH`.
-2. Installs autocompletion. This is entirely optional but pretty
+2. **Installs autocompletion.** This is entirely optional but pretty
useful. Sourcing `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.bash` will set that
up. There is also a `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.zsh` for Zsh
users.
-3. Rehashes shims. From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
+3. **Rehashes shims.** From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
shim files. Doing this on init makes sure everything is up to
date. You can always run `pyenv rehash` manually.
-4. Installs the sh dispatcher. This bit is also optional, but allows
+4. **Installs the sh dispatcher.** This bit is also optional, but allows
pyenv and plugins to change variables in your current shell, making
commands like `pyenv shell` possible. The sh dispatcher doesn't do
anything crazy like override `cd` or hack your shell prompt, but if
for some reason you need `pyenv` to be a real script rather than a
shell function, you can safely skip it.
-Run `pyenv init -` for yourself to see exactly what happens under the
-hood.
+To see exactly what happens under the hood for yourself, run `pyenv init -`.
+
### Uninstalling Python Versions
-As time goes on, Python versions you install will accumulate in your
+As time goes on, you will accumulate Python versions in your
`~/.pyenv/versions` directory.
To remove old Python versions, `pyenv uninstall` command to automate
the removal process.
-Or, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the
-version you want to remove. You can find the directory of a particular
-Python version with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix
-2.6.8`.
+Alternatively, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the version you want
+to remove. You can find the directory of a particular Python version
+with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix 2.6.8`.
+
## Command Reference
Like `git`, the `pyenv` command delegates to subcommands based on its
first argument. The most common subcommands are:
+
### pyenv local
Sets a local application-specific Python version by writing the version
@@ -304,6 +319,7 @@ file named `.pyenv-version`. For backwards compatibility, pyenv will
read a local version specified in an `.pyenv-version` file, but a
`.python-version` file in the same directory will take precedence.
+
#### pyenv local (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as local Python at once.
@@ -337,6 +353,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv global
Sets the global version of Python to be used in all shells by writing
@@ -352,6 +369,7 @@ The special version name `system` tells pyenv to use the system Python
When run without a version number, `pyenv global` reports the
currently configured global version.
+
#### pyenv global (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as global Python at once.
@@ -385,6 +403,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv shell
Sets a shell-specific Python version by setting the `PYENV_VERSION`
@@ -405,6 +424,7 @@ prefer not to use shell integration, you may simply set the
$ export PYENV_VERSION=pypy-2.2.1
+
#### pyenv shell (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions via `PYENV_VERSION` at once.
@@ -438,6 +458,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv versions
Lists all Python versions known to pyenv, and shows an asterisk next to
@@ -451,6 +472,7 @@ the currently active version.
jython-2.5.3
pypy-2.2.1
+
### pyenv version
Displays the currently active Python version, along with information on
@@ -459,6 +481,7 @@ how it was set.
$ pyenv version
2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
+
### pyenv rehash
Installs shims for all Python binaries known to pyenv (i.e.,
@@ -467,6 +490,7 @@ version of Python, or install a package that provides binaries.
$ pyenv rehash
+
### pyenv which
Displays the full path to the executable that pyenv will invoke when
@@ -475,6 +499,7 @@ you run the given command.
$ pyenv which python3.3
/home/yyuu/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/bin/python3.3
+
### pyenv whence
Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
@@ -483,7 +508,8 @@ Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
2.6.8
2.7.6
3.3.3
-
+
+
### pyenv install
Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-build), this installs versions of python
@@ -494,7 +520,8 @@ Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-
system
2.6.8
* 2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
-
+
+
### pyenv install --list
List available remote versions of Python, including Anaconda, Jython, pypy, and stackless
@@ -511,9 +538,10 @@ and easy to understand, even if you're not a shell hacker.
Please feel free to submit pull requests and file bugs on the [issue
tracker](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/issues).
+
### Version History
-See CHANGELOG.md.
+See [CHANGELOG.md](CHANGELOG.md).
### License
 +
+ +
### pyenv _does..._
@@ -20,6 +21,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* Search commands from **multiple versions of Python at a time**.
This may be helpful to test across Python versions with [tox](http://pypi.python.org/pypi/tox).
+
### In contrast with pythonbrew and pythonz, pyenv _does not..._
* **Depend on Python itself.** pyenv was made from pure shell scripts.
@@ -30,6 +32,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
yourself, or [pyenv-virtualenv](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-virtualenv)
to automate the process.
+
## Table of Contents
* [How It Works](#how-it-works)
@@ -56,6 +59,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* [Version History](#version-history)
* [License](#license)
+
## How It Works
At a high level, pyenv intercepts Python commands using shim
@@ -63,6 +67,7 @@ executables injected into your `PATH`, determines which Python version
has been specified by your application, and passes your commands along
to the correct Python installation.
+
### Understanding PATH
When you run a command like `python` or `pip`, your operating system
@@ -78,6 +83,7 @@ precedence over another one at the end. In this example, the
`/usr/local/bin` directory will be searched first, then `/usr/bin`,
then `/bin`.
+
### Understanding Shims
pyenv works by inserting a directory of _shims_ at the front of your
@@ -98,28 +104,30 @@ operating system will do the following:
* Run the shim named `pip`, which in turn passes the command along to
pyenv
+
### Choosing the Python Version
When you execute a shim, pyenv determines which Python version to use by
reading it from the following sources, in this order:
-1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable, if specified. You can use
+1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable (if specified). You can use
the [`pyenv shell`](#pyenv-shell) command to set this environment
variable in your current shell session.
2. The application-specific `.python-version` file in the current
- directory, if present. You can modify the current directory's
+ directory (if present). You can modify the current directory's
`.python-version` file with the [`pyenv local`](#pyenv-local)
command.
-3. The first `.python-version` file found by searching each parent
- directory until reaching the root of your filesystem, if any.
+3. The first `.python-version` file found (if any) by searching each parent
+ directory, until reaching the root of your filesystem.
4. The global `~/.pyenv/version` file. You can modify this file using
the [`pyenv global`](#pyenv-global) command. If the global version
file is not present, pyenv assumes you want to use the "system"
- Python—i.e. whatever version would be run if pyenv weren't in your
- path.
+ Python. (In other words, whatever version would run if pyenv weren't in your
+ `PATH`.)
+
### Locating the Python Installation
@@ -128,39 +136,43 @@ specified, it passes the command along to the corresponding Python
installation.
Each Python version is installed into its own directory under
-`~/.pyenv/versions`. For example, you might have these versions
-installed:
+`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
+For example, you might have these versions installed:
* `~/.pyenv/versions/2.7.6/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/pypy-2.2.1/`
-Version names to pyenv are simply the names of the directories in
+As far as pyenv is concerned, version names are simply the directories in
`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
## Installation
If you're on Mac OS X, consider
[installing with Homebrew](#homebrew-on-mac-os-x).
+
### The automatic installer
Visit my other project:
https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-installer
+
### Basic GitHub Checkout
This will get you going with the latest version of pyenv and make it
easy to fork and contribute any changes back upstream.
-1. Check out pyenv where you want it installed. A good place to choose is
+1. **Check out pyenv where you want it installed.** A good place to choose is
`$HOME/.pyenv` but you may install it somewhere else.
$ cd
$ git clone git://github.com/yyuu/pyenv.git .pyenv
-2. Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT` to point to the path where
+2. **Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT`** to point to the path where
pyenv repo is cloned and add `$PYENV_ROOT/bin` to your `$PATH` for access
to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
@@ -170,19 +182,19 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-3. Add pyenv init to your shell to enable shims and autocompletion.
+3. **Add `pyenv init` to your shell** to enable shims and autocompletion.
$ echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bash_profile
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-4. Restart your shell so the path changes take effect. You can now
+4. **Restart your shell so the path changes take effect.** You can now
begin using pyenv.
$ exec $SHELL
-5. Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`. For example, to
+5. **Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`.** For example, to
install Python 2.7.6, download and unpack the source, then run:
$ pyenv install 2.7.6
@@ -192,12 +204,13 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**NOTE** If you are having trouble installing a python version please visit the wiki page about [Common Build Problems](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/wiki/Common-build-problems)
-6. Rebuild the shim binaries. You should do this any time you install
- a new Python binary (for example, when installing a new Python version,
- or when installing a package that provides a binary).
+6. **Rebuild the shim binaries.** You should do this any time you install
+ a new Python binary. (Examples: installing a new Python version,
+ or installing a package that provides a binary.)
$ pyenv rehash
+
#### Upgrading
If you've installed pyenv using the instructions above, you can
@@ -217,23 +230,24 @@ tag:
v0.1.0
$ git checkout v0.1.0
+
### Homebrew on Mac OS X
You can also install pyenv using the
-[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS
-X.
+[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS X.
~~~
$ brew update
$ brew install pyenv
~~~
-To later update these installs, use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
+To upgrade pyenv in the future, just use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
-Afterwards you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
-profile as stated in the caveats. You'll only ever have to do this
+After installation, you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
+profile (as stated in the caveats). You'll only ever have to do this
once.
+
### Neckbeard Configuration
Skip this section unless you must know what every line in your shell
@@ -243,47 +257,48 @@ profile is doing.
extra commands into your shell. Coming from rvm, some of you might be
opposed to this idea. Here's what `pyenv init` actually does:
-1. Sets up your shims path. This is the only requirement for pyenv to
+1. **Sets up your shims path.** This is the only requirement for pyenv to
function properly. You can do this by hand by prepending
`~/.pyenv/shims` to your `$PATH`.
-2. Installs autocompletion. This is entirely optional but pretty
+2. **Installs autocompletion.** This is entirely optional but pretty
useful. Sourcing `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.bash` will set that
up. There is also a `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.zsh` for Zsh
users.
-3. Rehashes shims. From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
+3. **Rehashes shims.** From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
shim files. Doing this on init makes sure everything is up to
date. You can always run `pyenv rehash` manually.
-4. Installs the sh dispatcher. This bit is also optional, but allows
+4. **Installs the sh dispatcher.** This bit is also optional, but allows
pyenv and plugins to change variables in your current shell, making
commands like `pyenv shell` possible. The sh dispatcher doesn't do
anything crazy like override `cd` or hack your shell prompt, but if
for some reason you need `pyenv` to be a real script rather than a
shell function, you can safely skip it.
-Run `pyenv init -` for yourself to see exactly what happens under the
-hood.
+To see exactly what happens under the hood for yourself, run `pyenv init -`.
+
### Uninstalling Python Versions
-As time goes on, Python versions you install will accumulate in your
+As time goes on, you will accumulate Python versions in your
`~/.pyenv/versions` directory.
To remove old Python versions, `pyenv uninstall` command to automate
the removal process.
-Or, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the
-version you want to remove. You can find the directory of a particular
-Python version with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix
-2.6.8`.
+Alternatively, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the version you want
+to remove. You can find the directory of a particular Python version
+with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix 2.6.8`.
+
## Command Reference
Like `git`, the `pyenv` command delegates to subcommands based on its
first argument. The most common subcommands are:
+
### pyenv local
Sets a local application-specific Python version by writing the version
@@ -304,6 +319,7 @@ file named `.pyenv-version`. For backwards compatibility, pyenv will
read a local version specified in an `.pyenv-version` file, but a
`.python-version` file in the same directory will take precedence.
+
#### pyenv local (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as local Python at once.
@@ -337,6 +353,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv global
Sets the global version of Python to be used in all shells by writing
@@ -352,6 +369,7 @@ The special version name `system` tells pyenv to use the system Python
When run without a version number, `pyenv global` reports the
currently configured global version.
+
#### pyenv global (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as global Python at once.
@@ -385,6 +403,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv shell
Sets a shell-specific Python version by setting the `PYENV_VERSION`
@@ -405,6 +424,7 @@ prefer not to use shell integration, you may simply set the
$ export PYENV_VERSION=pypy-2.2.1
+
#### pyenv shell (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions via `PYENV_VERSION` at once.
@@ -438,6 +458,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv versions
Lists all Python versions known to pyenv, and shows an asterisk next to
@@ -451,6 +472,7 @@ the currently active version.
jython-2.5.3
pypy-2.2.1
+
### pyenv version
Displays the currently active Python version, along with information on
@@ -459,6 +481,7 @@ how it was set.
$ pyenv version
2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
+
### pyenv rehash
Installs shims for all Python binaries known to pyenv (i.e.,
@@ -467,6 +490,7 @@ version of Python, or install a package that provides binaries.
$ pyenv rehash
+
### pyenv which
Displays the full path to the executable that pyenv will invoke when
@@ -475,6 +499,7 @@ you run the given command.
$ pyenv which python3.3
/home/yyuu/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/bin/python3.3
+
### pyenv whence
Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
@@ -483,7 +508,8 @@ Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
2.6.8
2.7.6
3.3.3
-
+
+
### pyenv install
Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-build), this installs versions of python
@@ -494,7 +520,8 @@ Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-
system
2.6.8
* 2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
-
+
+
### pyenv install --list
List available remote versions of Python, including Anaconda, Jython, pypy, and stackless
@@ -511,9 +538,10 @@ and easy to understand, even if you're not a shell hacker.
Please feel free to submit pull requests and file bugs on the [issue
tracker](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/issues).
+
### Version History
-See CHANGELOG.md.
+See [CHANGELOG.md](CHANGELOG.md).
### License
+
### pyenv _does..._
@@ -20,6 +21,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* Search commands from **multiple versions of Python at a time**.
This may be helpful to test across Python versions with [tox](http://pypi.python.org/pypi/tox).
+
### In contrast with pythonbrew and pythonz, pyenv _does not..._
* **Depend on Python itself.** pyenv was made from pure shell scripts.
@@ -30,6 +32,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
yourself, or [pyenv-virtualenv](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-virtualenv)
to automate the process.
+
## Table of Contents
* [How It Works](#how-it-works)
@@ -56,6 +59,7 @@ This project was forked from [rbenv](https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv) and
* [Version History](#version-history)
* [License](#license)
+
## How It Works
At a high level, pyenv intercepts Python commands using shim
@@ -63,6 +67,7 @@ executables injected into your `PATH`, determines which Python version
has been specified by your application, and passes your commands along
to the correct Python installation.
+
### Understanding PATH
When you run a command like `python` or `pip`, your operating system
@@ -78,6 +83,7 @@ precedence over another one at the end. In this example, the
`/usr/local/bin` directory will be searched first, then `/usr/bin`,
then `/bin`.
+
### Understanding Shims
pyenv works by inserting a directory of _shims_ at the front of your
@@ -98,28 +104,30 @@ operating system will do the following:
* Run the shim named `pip`, which in turn passes the command along to
pyenv
+
### Choosing the Python Version
When you execute a shim, pyenv determines which Python version to use by
reading it from the following sources, in this order:
-1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable, if specified. You can use
+1. The `PYENV_VERSION` environment variable (if specified). You can use
the [`pyenv shell`](#pyenv-shell) command to set this environment
variable in your current shell session.
2. The application-specific `.python-version` file in the current
- directory, if present. You can modify the current directory's
+ directory (if present). You can modify the current directory's
`.python-version` file with the [`pyenv local`](#pyenv-local)
command.
-3. The first `.python-version` file found by searching each parent
- directory until reaching the root of your filesystem, if any.
+3. The first `.python-version` file found (if any) by searching each parent
+ directory, until reaching the root of your filesystem.
4. The global `~/.pyenv/version` file. You can modify this file using
the [`pyenv global`](#pyenv-global) command. If the global version
file is not present, pyenv assumes you want to use the "system"
- Python—i.e. whatever version would be run if pyenv weren't in your
- path.
+ Python. (In other words, whatever version would run if pyenv weren't in your
+ `PATH`.)
+
### Locating the Python Installation
@@ -128,39 +136,43 @@ specified, it passes the command along to the corresponding Python
installation.
Each Python version is installed into its own directory under
-`~/.pyenv/versions`. For example, you might have these versions
-installed:
+`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
+For example, you might have these versions installed:
* `~/.pyenv/versions/2.7.6/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/`
* `~/.pyenv/versions/pypy-2.2.1/`
-Version names to pyenv are simply the names of the directories in
+As far as pyenv is concerned, version names are simply the directories in
`~/.pyenv/versions`.
+
## Installation
If you're on Mac OS X, consider
[installing with Homebrew](#homebrew-on-mac-os-x).
+
### The automatic installer
Visit my other project:
https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv-installer
+
### Basic GitHub Checkout
This will get you going with the latest version of pyenv and make it
easy to fork and contribute any changes back upstream.
-1. Check out pyenv where you want it installed. A good place to choose is
+1. **Check out pyenv where you want it installed.** A good place to choose is
`$HOME/.pyenv` but you may install it somewhere else.
$ cd
$ git clone git://github.com/yyuu/pyenv.git .pyenv
-2. Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT` to point to the path where
+2. **Define environment variable `PYENV_ROOT`** to point to the path where
pyenv repo is cloned and add `$PYENV_ROOT/bin` to your `$PATH` for access
to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
@@ -170,19 +182,19 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-3. Add pyenv init to your shell to enable shims and autocompletion.
+3. **Add `pyenv init` to your shell** to enable shims and autocompletion.
$ echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bash_profile
**Zsh note**: Modify your `~/.zshenv` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
**Ubuntu note**: Modify your `~/.bashrc` file instead of `~/.bash_profile`.
-4. Restart your shell so the path changes take effect. You can now
+4. **Restart your shell so the path changes take effect.** You can now
begin using pyenv.
$ exec $SHELL
-5. Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`. For example, to
+5. **Install Python versions into `$PYENV_ROOT/versions`.** For example, to
install Python 2.7.6, download and unpack the source, then run:
$ pyenv install 2.7.6
@@ -192,12 +204,13 @@ to the `pyenv` command-line utility.
**NOTE** If you are having trouble installing a python version please visit the wiki page about [Common Build Problems](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/wiki/Common-build-problems)
-6. Rebuild the shim binaries. You should do this any time you install
- a new Python binary (for example, when installing a new Python version,
- or when installing a package that provides a binary).
+6. **Rebuild the shim binaries.** You should do this any time you install
+ a new Python binary. (Examples: installing a new Python version,
+ or installing a package that provides a binary.)
$ pyenv rehash
+
#### Upgrading
If you've installed pyenv using the instructions above, you can
@@ -217,23 +230,24 @@ tag:
v0.1.0
$ git checkout v0.1.0
+
### Homebrew on Mac OS X
You can also install pyenv using the
-[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS
-X.
+[Homebrew](http://brew.sh) package manager on Mac OS X.
~~~
$ brew update
$ brew install pyenv
~~~
-To later update these installs, use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
+To upgrade pyenv in the future, just use `upgrade` instead of `install`.
-Afterwards you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
-profile as stated in the caveats. You'll only ever have to do this
+After installation, you'll still need to add `eval "$(pyenv init -)"` to your
+profile (as stated in the caveats). You'll only ever have to do this
once.
+
### Neckbeard Configuration
Skip this section unless you must know what every line in your shell
@@ -243,47 +257,48 @@ profile is doing.
extra commands into your shell. Coming from rvm, some of you might be
opposed to this idea. Here's what `pyenv init` actually does:
-1. Sets up your shims path. This is the only requirement for pyenv to
+1. **Sets up your shims path.** This is the only requirement for pyenv to
function properly. You can do this by hand by prepending
`~/.pyenv/shims` to your `$PATH`.
-2. Installs autocompletion. This is entirely optional but pretty
+2. **Installs autocompletion.** This is entirely optional but pretty
useful. Sourcing `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.bash` will set that
up. There is also a `~/.pyenv/completions/pyenv.zsh` for Zsh
users.
-3. Rehashes shims. From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
+3. **Rehashes shims.** From time to time you'll need to rebuild your
shim files. Doing this on init makes sure everything is up to
date. You can always run `pyenv rehash` manually.
-4. Installs the sh dispatcher. This bit is also optional, but allows
+4. **Installs the sh dispatcher.** This bit is also optional, but allows
pyenv and plugins to change variables in your current shell, making
commands like `pyenv shell` possible. The sh dispatcher doesn't do
anything crazy like override `cd` or hack your shell prompt, but if
for some reason you need `pyenv` to be a real script rather than a
shell function, you can safely skip it.
-Run `pyenv init -` for yourself to see exactly what happens under the
-hood.
+To see exactly what happens under the hood for yourself, run `pyenv init -`.
+
### Uninstalling Python Versions
-As time goes on, Python versions you install will accumulate in your
+As time goes on, you will accumulate Python versions in your
`~/.pyenv/versions` directory.
To remove old Python versions, `pyenv uninstall` command to automate
the removal process.
-Or, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the
-version you want to remove. You can find the directory of a particular
-Python version with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix
-2.6.8`.
+Alternatively, simply `rm -rf` the directory of the version you want
+to remove. You can find the directory of a particular Python version
+with the `pyenv prefix` command, e.g. `pyenv prefix 2.6.8`.
+
## Command Reference
Like `git`, the `pyenv` command delegates to subcommands based on its
first argument. The most common subcommands are:
+
### pyenv local
Sets a local application-specific Python version by writing the version
@@ -304,6 +319,7 @@ file named `.pyenv-version`. For backwards compatibility, pyenv will
read a local version specified in an `.pyenv-version` file, but a
`.python-version` file in the same directory will take precedence.
+
#### pyenv local (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as local Python at once.
@@ -337,6 +353,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv global
Sets the global version of Python to be used in all shells by writing
@@ -352,6 +369,7 @@ The special version name `system` tells pyenv to use the system Python
When run without a version number, `pyenv global` reports the
currently configured global version.
+
#### pyenv global (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions as global Python at once.
@@ -385,6 +403,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv shell
Sets a shell-specific Python version by setting the `PYENV_VERSION`
@@ -405,6 +424,7 @@ prefer not to use shell integration, you may simply set the
$ export PYENV_VERSION=pypy-2.2.1
+
#### pyenv shell (advanced)
You can specify multiple versions via `PYENV_VERSION` at once.
@@ -438,6 +458,7 @@ or, if you prefer 3.3.3 over 2.7.6,
$ python3.3 --version
Python 3.3.3
+
### pyenv versions
Lists all Python versions known to pyenv, and shows an asterisk next to
@@ -451,6 +472,7 @@ the currently active version.
jython-2.5.3
pypy-2.2.1
+
### pyenv version
Displays the currently active Python version, along with information on
@@ -459,6 +481,7 @@ how it was set.
$ pyenv version
2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
+
### pyenv rehash
Installs shims for all Python binaries known to pyenv (i.e.,
@@ -467,6 +490,7 @@ version of Python, or install a package that provides binaries.
$ pyenv rehash
+
### pyenv which
Displays the full path to the executable that pyenv will invoke when
@@ -475,6 +499,7 @@ you run the given command.
$ pyenv which python3.3
/home/yyuu/.pyenv/versions/3.3.3/bin/python3.3
+
### pyenv whence
Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
@@ -483,7 +508,8 @@ Lists all Python versions with the given command installed.
2.6.8
2.7.6
3.3.3
-
+
+
### pyenv install
Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-build), this installs versions of python
@@ -494,7 +520,8 @@ Part of [Python-build](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/tree/master/plugins/python-
system
2.6.8
* 2.7.6 (set by /home/yyuu/.pyenv/version)
-
+
+
### pyenv install --list
List available remote versions of Python, including Anaconda, Jython, pypy, and stackless
@@ -511,9 +538,10 @@ and easy to understand, even if you're not a shell hacker.
Please feel free to submit pull requests and file bugs on the [issue
tracker](https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv/issues).
+
### Version History
-See CHANGELOG.md.
+See [CHANGELOG.md](CHANGELOG.md).
### License